- Seen : 587 View
Production of gas condensate or air separation Air Separation Unit: It is called the method of separating atmospheric air into its components including nitrogen, oxygen and argon.
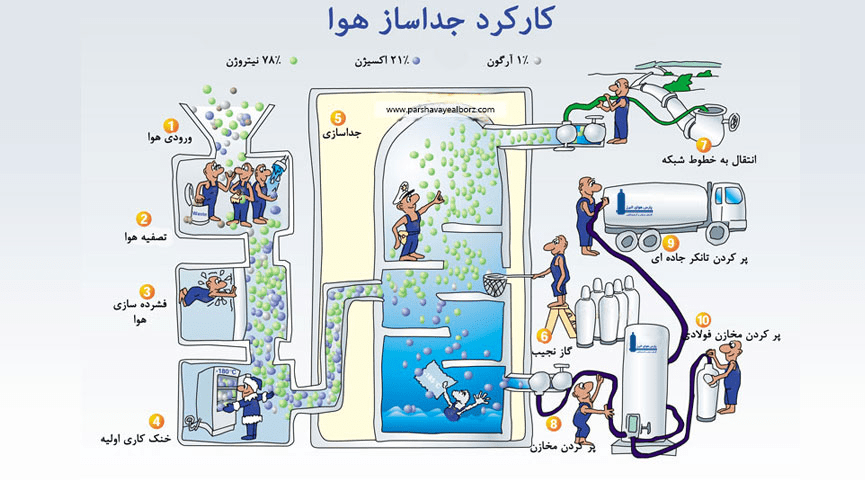
Earth's atmosphere consists of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and less than 1% argon.
Due to the increasing use of oxygen, its production rate now ranks third in the production of chemicals in the world. The applications of nitrogen, oxygen and argon gas condensates can be mentioned in industries such as steel, glass, welding and cutting, health and treatment, food, metallurgy, glass, petrochemical and refinery industries, oil and gas, etc.
The most common method of air separation is cryogenic or distillation method. Other methods such as: chemical process, membrane separation and surface absorption are used to separate a component from atmospheric air. Basically, nitrogen, oxygen and argon are produced with high purity by cryogenic method. In this method, the air enters the compressor after removing the pollutants and purifying it.
Then, according to the turbines after the air compressor, the pressure decreases and then it cools down to a very low temperature of -196 degrees Celsius, and then it goes to the distillation tower, where it is formed according to the different boiling temperatures of the elements. The donor (oxygen-183), (nitrogen-196) and argon-186 are separated and the mentioned products are produced.
In order to reach low temperature in distillation, cooling equipment, insulated chamber and a refrigeration cycle, which operates using the Joule-Thomson method, are needed.
The distillation process includes the following steps:
Air enters the system with these specifications. 99% of its volume is made up of oxygen and nitrogen gases and the remaining gases include argon, carbon dioxide, xenon and other noble gases.
In order to remove impurities, the air is pre-filtered before it is separated into its component parts.
Air is sucked in at a pressure of about 5 to 10 bar. Different pressures are for different efficiencies.
In this section, the initial cooling of the air is done up to -180 ºC. As the air rises in the liquid column, it cools until it becomes a liquid.
In the distillation column, air is converted into its components in a completely physical process. The liquid collects on the column of the tray. First, oxygen condenses with a higher boiling temperature (-183 ºC), then nitrogen tends to condense with a lower boiling temperature (-196 ºC). Nitrogen gases are collected at the top of the column and liquid oxygen at the bottom of the column. Oxygen evaporates at the bottom, while nitrogen is condensing at the top. This process continues until we reach the desired level of purity.
Produced oxygen and nitrogen enter the network lines with a pressure of 40 bar. Liquid oxygen, nitrogen and argon are filled inside the tanks. Part is transferred to road tankers and another part enters steel tanks with a pressure of 300 bar.
Carbon dioxide is another thing that can be used in liquid form in various industries, so it is used to produce carbon dioxide by burning hydrocarbons and the exhaust of industrial units.
Saler Company Information










